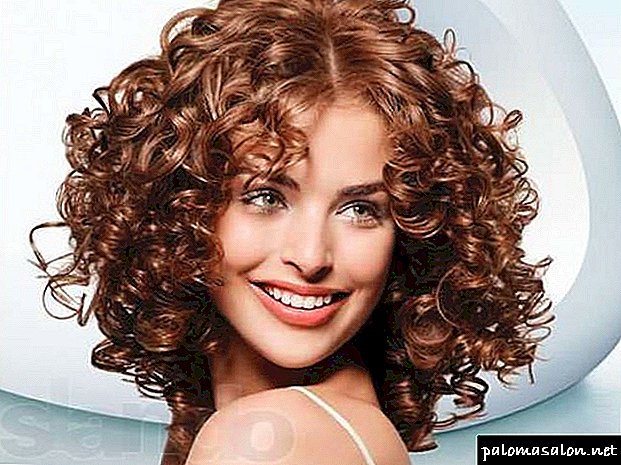
Scalp dermatitis is a disease that many people suffer from. Most often the disease manifests itself in the form of ordinary dandruff. Most people who have long suffered from pathology simply do not pay attention to it, considering dandruff as the norm. This attitude to the disease is wrong, as dermatitis of the scalp can lead to complete loss of hair. To avoid this, you need to know exactly what kind of disease the person suffers and what methods the disease is treated.

Why dermatitis occurs
There are many reasons due to which a disease of the scalp occurs. It may be:
- Changes in hormone levels, hormonal disruptions. Most often, this cause leads to the development of dermatitis of the scalp in adolescence. This is due to the fact that the level of hormones in the blood of the growing up girls and boys increases, which leads to increased work of the sebaceous and sweat glands. Due to the abundance of secretions on the body of a teenager, various skin problems begin. Microorganisms love such an environment, causing various violations of the epidermis.
- Similar causes cause dermatitis of the scalp in infants. Baby gets hormones with mother's milk. As a result, the intensive work of the sebaceous and sweat glands can occur, which causes dermatitis.
- Heredity. Scientists have shown that the principles of the sebaceous glands in relatives are similar, so seborrhea is often called a family disease.
- Immune weakening. This cause can cause a variety of ailments, including the development of dermatitis. Typically, a decrease in immune protection occurs only through the fault of the person himself, in rare cases due to pathologies.
Also leading to the development of pathology may be shampooing with poor-quality shampoos, stress, climate change, wearing different hats, intense exercise and much more. Uncontrolled intake of certain medications, in particular antibiotics, used without a prescription may lead to dermatitis.

Types of dermatitis
Seborrhea of the scalp is divided into several types:
- Dry dermatitis. This type is most often diagnosed in adolescents. The skin is dry, cracking.
- Bold look. This kind of manifestation occurs most often in women. Oily dermatitis is manifested in the form of excessive secretions by the glands of the scalp, resulting in permanent contamination of hair and skin.
- Mixed look. Manifested in the form of dryness of some areas and the fat content of others.
Other manifestations of the disease
Scalp dermatitis can affect symmetrically the boundaries of the eyelashes and eyebrows. When this type of lesion manifests itself diffusely or focal plaques of different diameters. If there is no inflammation in the disease, the dermatitis is considered dry. Sometimes, due to dry skin, patients start washing their hair less and less. Because of this, scales begin to form, which intensifies dermatitis and aggravates the overall situation.
In the oily variety of seborrhea, dense, yellow scales are observed adjacent to the skin. If you do not begin treatment for seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp, then it becomes severe. Inflamed areas will be affected by sebum, causing the scales to thicken and thicken. As a result, erosion appears under them, the skin begins to itch, an infection joins. This phenomenon is called seborrhoeic eczema. To prevent this from happening, you need to consult a doctor. He will determine the exact form of the disease and prescribe the correct treatment for seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp.

Clinical manifestations
The symptoms of dermatitis are as follows:
- Dandruff. This is the main symptom of the disease, which signals that something is wrong with the scalp. Dandruff causes hair loss. Some scales can stick to the skin, and some remain on the hair.
- Skin irritation. On the head there are spots with distinct edges. As the disease develops, these islets gradually begin to dry out and heal, crusts form on them. This phenomenon is caused by the activity of a fungal infection.
- Puffiness When you move the disease in those areas where there are folds, there is swelling. With dermatitis of the head, such a manifestation is observed with skin lesions in the ear area.
- Peeling. As the skin heals, a strong flaking begins. It is accompanied by an itch that does not stop even for a short time. This happens because of the rapid rejection of cells.
- Scales. This symptom has been observed since the first days of dermatitis. Scales gather on the head like a crown. This clinical sign is observed due to soaking dry areas in the sebum. With the onset of pathology, the scales are small, they are white. As the disease progresses, they become more, they turn yellow.
- Rash on the skin. When an infection is attached, a rash appears on the scalp. It usually has watery contents, but purulent pimples are not rare.
Treatment methods
Treatment of dermatitis of the scalp is reduced to the use of a variety of drugs, shampoos, folk remedies. In some cases, may require hormone therapy, the use of physiotherapy. Mandatory prescribed medical nutrition for seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp.

For successful treatment of the disease, the scalp is scraped to determine the type of pathogen. After that, an antifungal drug is prescribed. Antifungal shampoos are successfully used. They help eliminate itching, burning, partially relieve dandruff. To get rid of atopic dermatitis of the scalp, apply a variety of creams, oils and not only.
Dermatitis Shampoos
Shampoo is an integral part of successful dermatitis treatment. It is used in the treatment of disease in conjunction with other means. Shampoos for seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp are divided into the following groups:
- Selenium - have anti-fungal effects.
- Ketonazol - inhibits the growth of the fungus.
- Zinc pyrithione - able to fight inflammatory processes and accelerate the healing of damaged skin.
- Tar - eliminates peeling, itching.
- Cyclopirox - has an effect on the pathogen.
Shampoo overview
Pharmaceutical manufacturing companies offer a huge range of a variety of shampoos for scalp dermatitis, including the following:
- Keto Plus. Shampoo gives positive results in the treatment of the disease, but only if the use of the agent starts at the very beginning of the ailment. The manufacturer recommends using it for at least a month. "Keto Plus" is a combination product: it is easy to apply and just as easily washed off. It is an antifungal agent.
- "Nizoral". The tool is well proven in the treatment of dermatitis and other skin pathologies. The shampoo has a strong anti-inflammatory effect. After treatment, the causes of the disease are eliminated. This shampoo can be used to treat dermatitis of the baby’s scalp, as well as pregnant women.
- "Skin Cap". Shampoo is recommended for the treatment of oily seborrhea. It dries the skin well, relieves itching.
- "Ducrey". Used to treat dry seborrhea. Helps to cope with itching, relieves irritation of the skin, fights dandruff.
- "Friderm." It shows high efficacy in the treatment of oily seborrhea. The shampoo has a pronounced woody fragrance, which passes after washing off the product with a strand.

Traditional methods of treatment
You can get rid of dermatitis by folk methods. They help relieve itching, burning, inflammation, clear skin of scales. Such methods affect different types of diseases in different ways. Here are some traditional medicine recipes that help in the fight against seborrhea:
- The infusion of the series. This tool helps to cope with severe itching. Most often, the series is used for bathing children, adding an infusion to the bath. It can also be used as a lotion.
- Infusion Altea root. For the preparation of funds will need seven grams of a plant pour a glass of boiling water and let it brew for an hour. After this infusion moisten gauze and applied to the affected areas.
- Sage tea. For the preparation of funds take five grams of raw materials, and pour a glass of boiling water. The product is boiled for five minutes, then allowed to brew for 30 minutes. Filter the finished product, add a little honey. The composition is used as lotions.
- Infusion of hypericum and burdock. For cooking means you need to take three tsp. burdock root, the same amount of Hypericum and elecampane. All herbs are mixed. Then 4 teaspoons of the mixture is poured a glass of boiling water and insist night. The resulting mixture should be rubbed into the head after each wash. Do not flush.

Other recipes
- Nettle decoction. It will take half a liter of water, the same vinegar, one hundred grams of nettle. The composition is placed for half an hour on fire. Then the agent is allowed to cool. Apply in the form of lotions.
- Dandelion juice. When dermatitis of the scalp is recommended to drink at least three times a day mixed with water dandelion juice (a tablespoon). From the leaves of the plant can be infused. For him, take a spoonful of leaves and pour two cups of boiling water. Then the agent is allowed to infuse for an hour. It is taken in half a glass every three hours.
- Ointment with hypericum. To prepare it, you must take the juice of Hypericum and evaporate it halfway, add butter to the resulting volume, approximately in the ratio 1: 4, and mix everything. The tool is placed in the fridge. Ointment smear the affected areas.
- Ointment from the juice of plantain. Plantain juice is taken and mixed in half with Vaseline. Everything is mixed, covered tightly with a lid. The tool is stored in the refrigerator.
- Well helps to cope with dermatitis decoction of oak bark, sage, chamomile extract, which are able to effectively fight dandruff. When using this tool should abandon the usual shampoos.

Nutritional Features of Dermatitis
During any pathology, it is important to adhere to the correct daily routine. This concerns not only physical activity, but also sleep, walking, nutrition. Patients with seborrheic dermatitis are forbidden to eat fried, fatty, sweet. You should also abandon the white bread, which can provoke a more enhanced manifestation of dermatitis. The diet should be low-calorie foods low in carbohydrates. Sugar and salt consumption is desirable to reduce to zero. Doctors recommend a protein diet, including boiled meat in your diet. It is useful to add to the menu more vegetables and fruits, dairy products.
Conclusion
Knowing how to treat dermatitis of the scalp, you can once and for all get rid of the pathology. To this end, it is necessary to do two things: firstly, to visit a doctor, and secondly, to strictly follow all his recommendations. After the doctor determines the type of pathogen dermatitis, he will prescribe therapy, select the right shampoo, recommend decoctions, balms, masks and other means to care for the scalp. If necessary, a dermatologist or trichologist will select drugs for oral administration and prescribe other methods of treatment, such as hormone therapy, physical therapy, sanatorium-resort therapy.
What is dermatitis?
Seborrhea is the inflammation of the skin in the areas where the sebaceous glands are located. Pathology is chronic and prone to relapses in the autumn and spring periods. Dermatitis on the head can occur at any age, even in infants. However, more often the disease develops in men, and the overall prevalence of pathology is only up to 5%. In the presence of seborrhea, the patient is diagnosed with high sebum production, which serves as an excellent medium for reproduction of pathogenic microorganisms, and inflammation of the scalp.
Dermatitis of the scalp
As a rule, seborrhea first appears in a dry form, accompanied by abundant scaling (dandruff). When moving to the next stage, the disease acquires additional clinical signs - itching and discomfort. As a result of scratching on the head, wounds are formed, which serve as gates for infection and can fester. Hair becomes greasy and the patient often has to wash them to maintain a neat appearance of the hairstyle.
Subsequently, seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp becomes the cause of yellowish or white plaques that gradually grow. Scales covering plaques can stick together with each other and be barely visible on the scalp. After scraping the plates on the skin are found inflamed reddened areas. During the progression of seborrhea pathology causes active hair loss, in some cases, people form large bald areas. After the transition of the disease to a latent state, vegetation growth resumes.

The main causative agent of seborrheic dermatitis is an infection - the fungus Pityrosporum ovale, which is present on the skin of almost every person, but is activated only when the sebaceous glands increase and the immunity decreases. In order to maintain vital activity and reproduction, microorganisms use sebum, which can be stimulated by an external or internal factor. The latter include:
- pathology of the nervous system,
- endocrine disruptions
- immunity disorders (immunodeficiency),
- Parkinson's disease
- epilepsy.
The disease can occur under the influence of external factors:
- excessive sweating
- hereditary disposition,
- lack of zinc in the diet,
- vitamin deficiency vitamin PP,
- unbalanced nutrition
- hypothermia head
- stresses
- the use of alkaline products (as part of household chemicals or personal care products).
The clinical picture of the disease depends on the type of the disease, as well as on the location of the lesions. When dermatosis is located in the scalp, redness and rash are often accompanied by dandruff and hair loss. Foci of pathology may eventually merge and spread in the peripheral direction, as a result of which inflammatory areas appear on the skin, occupying a large area. The patient begins to feel a strong itching, soreness.
After scratching the inflamed areas, seborrhea is sometimes complicated by suppuration after the addition of a secondary infection. Most dermatologist patients note that exacerbation of dermatitis usually occurs as a result of a violation of the diet, abuse of spices, alcohol, sweets, spicy foods. After the resumption of dietary nutrition, the symptoms subside, and the healing process is accelerated. As a rule, the prognosis for seborrheic dermatitis is favorable.

Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp
Treat the disease should be a complex, which uses the methods of traditional and traditional medicine. The first thing the doctor advises to do to the patient is to normalize the diet, adding food with a high percentage of zinc and vitamins to the menu.Treatment of seborrhea of the scalp takes place with the mandatory use of antifungal drugs such as Nizoral, Fluconazole, Mikozorala, etc.
Patients whose lesions on the skin of the head are too extensive are given compresses, which soften dense scales. After that apply local antifungal therapy. The main task in the treatment of seborrhea is to get rid of the unpleasant symptoms of the pathology, that is, to eliminate itching, peeling and relieve inflammation. So, to cure dermatitis of the scalp, apply:
- antifungal cream / ointment, which is complemented by regular hygiene and skin care (cleansing, nutrition, moisturizing),
- systemic antifungal medications (if local remedies have proven ineffective),
- retinoid ointments or tablets (with the spread and transition of the disease into acne on the face, near the ear),
- immunomodulators for severe exacerbations of the pathology or accession of infection,
- sprays, powders, zinc-based ointments (help regulate the functioning of the sebaceous glands),
- Vitamins E and A, contributing to the process of exfoliation and skin renewal.
Moist and dry dermatitis should be treated with local remedies. In this case, the doctor individually prescribes a course of therapy, choosing a drug suitable group. Ointment for seborrheic dermatitis on the head can be hormonal or non-hormonal. Some tools can be used to treat a child, a pregnant or nursing mother (information about this is contained in the annotation to each tool). The most effective ointment against seborrheic dermatitis is:
- Sulfuric ointment. Means carefully grease the entire surface of the skin of the skull. Treat seborrhea with this tool for 8 days, followed by 1 day of rest. The next day, wash your hair with shampoo against dandruff. The next week the lesion site is treated with a solution of boric acid (per 100 ml of 1.5 tsp). The drug allows you to quickly get rid of the symptoms of seborrhea, eliminating itching, inflammation and desquamation.
- Lamisil. This is an affective antifungal agent that is applied to the affected areas of the scalp at intervals of 12 hours. The drug is often prescribed for the treatment of moist seborrhea.
- Elidel. An expensive drug is extremely effective against dermatitis on the head: it quickly relieves itching, eliminates inflammation and eliminates desquamation. In addition, the ointment kills fungi and is equally effective against any type of disease.
- Hydrocortisone ointment. Appointed to relieve itching, swelling and inflammation. Apply the product should be a thin layer 2 times a day. At the same time, it is necessary to treat dermatitis for at least 2-3 weeks. It is forbidden to apply the drug on the pustules.
- Flucinar It belongs to a group of antifungal agents, in addition, it can be used to treat allergies and relieve localized skin inflammations. Flucinar should be treated for seborrhea within 2 weeks.
- Nizoral The active ingredient of the drug is ketoconazole, which quickly suppresses fungi. It can be used for dry or oily seborrhea, while the therapeutic effect becomes noticeable after 10-12 days of use.

Another way to restore the scalp is to ensure proper hair care, for which medical shampoos are used. What remedies are most effective for treating and preventing dermatitis? Have earned a good reputation:
- Keto plus This combined antifungal medication is available in 60 ml bottles. Keto plus eliminates the symptoms of the disease, including desquamation and itching. The active substance of the shampoo destroys the walls of the fungus, and zinc prevents the division of pathogenic microbes. The cost of funds is about 500 rubles.
- Sulsen shampoo. The tool can be used for the treatment and prevention of dermatitis. Shampoo effectively fights pathogenic bacteria, eliminates the symptoms of the disease, restores healthy, well-groomed appearance to hair. The cost of funds from dermatitis is about 300 rubles.
- Nizoral shampoo. Thanks to ketoconazole in the preparation, it inhibits the synthesis of ergosterol and phospholipids, which help fungi to multiply. In addition, shampoo is an excellent anti-inflammatory drug and is able to normalize sebum production. Price Nizoral is about 600 rubles.
- Friderm Tar. The shampoo has anti-fungal and anti-proliferative effects. It helps to remove epidermal flakes from the head and is used, as a rule, to treat oily seborrhea. The cost of the product from dermatitis is about 700 rubles.
- Mycozoral The drug acts to eliminate dandruff, itching, restoration of the skin and hair. Shampoo kills fungi, relieves irritation, swelling, due to its effects hairs stop peeling off. The price of dermatitis on the head is 350 rubles.
Folk remedies
There are many factors due to which the use of drugs for the treatment of dermatitis is contraindicated. These include pregnancy, lactation, infancy, etc. For the treatment of the disease in infants and women who are breastfeeding or bearing a fetus, they use effective folk remedies that involve the use of natural ingredients. The most effective among them are:
Symptoms of dermatitis on the head
Seborrheic dermatitis of the head has the following symptoms:
- Severe itching
- The appearance of red scaly spots,
- Spots rapidly increase and have no clear boundaries
- Dry skin
- Skin tightness can be felt.
Atopic dermatitis of the head has several other symptoms, namely:
- Severe itching, sometimes long before rash appears,
- The skin is covered with dark red scales,
- Rashes appear not only on the head, but also on the face and body. In women, redness often occurs in the décolleté area,
- There are cases when the reddening turns into small bubbles, which later form thin crusts.
Allergic type of dermatitis
Allergic dermatitis may occur due to such reasons:
- Incorrectly chosen or low-quality shampoo, balm and other hair care products.
- Headgear, which is made of low-quality material.
- Food allergies: most often citrus fruits, exotic fruits, chocolate, as well as fish and seafood.
- Frequent stress and nervous strain can cause atopic dermatitis on the head.
- Long-term treatment with antibiotics and potent drugs.

And if in an adult the causes of occurrence are very easy to determine, then a child’s dermatitis may appear due to frequent washing with water or after sweating, since the skin is very sensitive and tender.
Dermatitis can also be congenital, in such cases, children have a rash, not only on the scalp, but throughout the body.
To diagnose allergic dermatitis is possible only after a detailed examination of the skin. And the treatment itself must be prescribed by a dermatologist or allergist. To confirm the diagnosis, it is necessary to pass tests and tests.
Allergic dermatitis on the head should be distinguished from depriving, psoriasis and seborrhea. In addition to conducting skin tests, you should pay attention to the state of the hormonal system, the state of immunity, and also to conduct a study for the presence of fungus.
The development of dermatitis on the head may indicate the presence of serious health problems, it is not necessary to self-medicate, and immediately contact the clinic.
Atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis can occur not only on the head, but also on the whole body. Often affects infants. At the same time, dermatitis spreads throughout the body, which brings great suffering to the child.

The appearance of atopic dermatitis of the scalp only is associated with the microflora of the skin. This means that the bacteria, fungi that we have in the body, for some reason, begin to show their disease-causing properties. And the reasons may be:
- genetics. A certain predisposition of the organism that does not resist infection. Heredity often causes allergic dermatitis on the head,
- a significant decline in the immune system
- chronic diseases of the nervous system. Very often, atopic dermatitis affects the scalp after a stroke, polyneuropathy,
- alcohol abuse
- hormonal disorders of the body.
It is not recommended to treat dermatitis yourself, because it can cause irreversible effects.
For atopic dermatitis of the scalp, a characteristic feature is severe itching, severe dryness of the skin and a large number of scales on the scalp, more information about this type of dermatitis can be found in the video.
What does dermatitis look like on the scalp?
During dermatitis, the epidermis of the scalp suffers greatly. The disease even in the early stages is very noticeable.
Dermatitis of the scalp can have these types:
- Dermatitis is fat. A type of dermatitis that causes permanent hair pollution and often happens in women.
- Dry skin dermatitis. May occur with a strong overdrying of the scalp, often found in adolescents and children. In this species, the skin is very cracking, there is a feeling of tightness.
- Mixed dermatitis. When on the scalp there are areas of dry and oily skin at the same time.

There are some factors that influence the development of dermatitis, and during treatment they pay great attention to them:
- Improper nutrition
- Lack of vitamins and minerals
- Insufficient amount of zinc in the body,
- Excessive sweating.
All these factors can influence the appearance or aggravate the situation in the presence of atopic dermatitis of the scalp.
And although the diagnosis is to take place at the doctor, treatment for skin lesions can be performed at home. But the physician should warn about what products should be avoided at the time of treatment and how to cope with the disease quickly.
What is seborrheic dermatitis?
Seborrheic dermatitis (seborrheaseborrheic eczema) is called inflammation of the skin in the locations of the sebaceous glands, which in most cases occurs chronically and has a tendency to exacerbate in spring or autumn.
This disease can occur at any age, even in infancy. According to statistics, seborrhea is more common for men. The prevalence of seborrheic dermatitis is about 2-5% among the world's population.
With seborrheic dermatitis the patient has increased sebum production and inflammation of the skin area. Sebum is an excellent medium for the growth of many pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic microorganisms, which provoke the inflammatory process of the skin. Therefore, the zones of seborrheic inflammatory process are usually located on areas of skin richly equipped with sebaceous glands: back, chest, some areas of the face, skin under the scalp.
In some cases, seborrhea can lead to various complications:
- alopecia (focal balding),
- furunculosis,
- dandruff
- blepharitis or conjunctivitis,
- otitis, etc.
Causes of seborrheic dermatitis
 The main cause of seborrheic dermatitis is an infectious agent. These are fungi Pityrosporum ovale, which are present in the form of spores on the skin in 90% of people, but begin their active growth only with increased production of sebaceous secretion by the skin and a decrease in local or general immunity. For their vital activity and reproduction, fungi actively use sebum and can cause inflammation of the skin.
The main cause of seborrheic dermatitis is an infectious agent. These are fungi Pityrosporum ovale, which are present in the form of spores on the skin in 90% of people, but begin their active growth only with increased production of sebaceous secretion by the skin and a decrease in local or general immunity. For their vital activity and reproduction, fungi actively use sebum and can cause inflammation of the skin.
Predisposing factors to active and excessive secretion of the sebaceous secretion can be internal and external factors.
Internal factors:
- endocrine diseases
- diseases of the nervous system
- epilepsy,
- Parkinson's disease,
- immunity disorders (HIV, AIDS, congenital immunodeficiency, etc.).
External factors:
- genetic predisposition to seborrhea,
- hyperhidrosis (excessive sweating),
- cold air,
- poor nutrition,
- low zinc content in the diet,
- PP avitaminosis,
- stressful situations
- the use of alkaline detergents in everyday life and for personal hygiene.
In many cases, eliminating the cause of seborrheic dermatitis helps to completely get rid of this skin disease or reduce its progression and relapse to a minimum.
Symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis
The severity and characteristics of symptoms of seborrheic dermatitis depends on the type of the disease, the location of the inflamed areas of the skin.
When localized on the scalp, rashes and redness may be accompanied by dandruff and hair loss. Seborrheic dermatitis in other areas of the skin is characterized by the appearance of clearly defined areas of redness with pink papules and plaques, which then become covered by skin scales, which are glued together by a greasy secret.
Lesions tend to merge and spread in the peripheral direction. As a result of this, inflamed zones of considerable size are formed on the skin, which cause discomfort in the patient, severe itching or soreness.
Scratches or injuries of skin areas affected by seborrheic eczema may be complicated by the addition of secondary infection and suppurations, and when localized on the wings of the nose, eyebrows, auricles, or in the auditory canal, inflammatory diseases of the nasopharynx, eyelids and ears.
Many patients note that the symptoms of seborrhea may worsen with dietary disorders and the abuse of alcoholic beverages, spices, spicy and sweet foods. When correcting the diet, symptoms subside and the healing process is accelerated.
The prognosis of seborrheic dermatitis is in most cases favorable.
Face dermatitis
In the first case, the skin becomes dry, and characteristic crusts form on it, which are difficult to get rid of using conventional care products.
With fatty type of seborrheic dermatitis in adults there is an increased oily skin. At the same time, some areas of the skin strongly shine and acquire a grayish tint. The relief of the skin becomes similar to the "orange peel", there are blackheads, which can become inflamed when attaching a secondary infection, forming acne and boils.
The main symptom of this disease can be considered the appearance of rashes on a certain area of the skin of the face in the form of noticeable pink papules 5 to 20 mm in diameter. Rashes have clear contours, and the skin on which they are located, with time begins to peel off. Inflammation of the skin is accompanied by a feeling of discomfort and itching.
The progression of lesions and untimely started treatment leads to the growth and merging of inflammatory foci. Layering of a secondary infection that flows into pyoderma is also possible. With the defeat of seborrheic dermatitis of the eyelid skin, blepharitis or conjunctivitis may develop.
The most characteristic areas of localization of lesions of seborrheic dermatitis are:
- nose,
- nasolabial folds,
- eyebrows and eyebrows,
- the area above the lip
- cheekbones.
But any sebaceous glands can be involved in the pathological process, so sometimes foci of seborrheic dermatitis can occur in other parts of the face.
Scalp Dermatitis
 Seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp initially appears in a dry form, which is accompanied by the appearance of dandruff. At the next stage of the disease, areas of redness appear on the scalp, which is accompanied by unpleasant sensations and itching.
Seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp initially appears in a dry form, which is accompanied by the appearance of dandruff. At the next stage of the disease, areas of redness appear on the scalp, which is accompanied by unpleasant sensations and itching.
When combing on the scalp, bleeding wounds may form, which, when attaching a secondary infection, suppurate. His hair quickly falls down, especially on their root part, and the patient begins to notice that he has to wash his hair more often in order to keep his appearance neat.
Further, on the sites of inflammation appear plaques milky or yellow, which gradually grow. Scales of plaques can be hardly noticeable and stick together with sebum between themselves and the scalp. Scraping such flakes on the head reveals an inflamed area of red skin.
With the progression and prolonged course of seborrheic dermatitis of the scalp, hair loss increases, and in some cases baldness areas of various sizes appear.
When subsiding the inflammatory process, hair growth in these areas, as a rule, resumes.
Treatment of dermatitis of the scalp
Treatment of dermatitis of the scalp is carried out comprehensively:
1. Diet is prescribed (it is recommended to introduce foods rich in zinc, vitamins A, B, C and PP, selenium into the diet).
2. The use of an antifungal drug (Nizorex, Mycozoral, Sebasol, Nizoral, Ketoconazole, Dermazole, etc.) in the form of a cream, gel or shampoo is recommended.
3. Antifungal antiseptics are prescribed (tar soap, zinc paste, bitter extract of Quassia, tea tree oil, etc.).
4. Recipes of traditional medicine can be applied.
Along with this treatment is the therapy of the underlying disease, which contributes to the development of seborrhea. As far as possible, predisposing factors (stress, hypothermia, unhealthy diet, etc.) are eliminated.
Shampoos for seborrheic dermatitis The modern cosmetic and pharmacological industry produces a wide range of shampoos for the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis: Nizoral, Ketoconazole, Skin cap, Squafan S, Sulsena, Tsinovit, Kelyual DS, Friederm Zinc, Danex, etc.
The modern cosmetic and pharmacological industry produces a wide range of shampoos for the treatment of seborrheic dermatitis: Nizoral, Ketoconazole, Skin cap, Squafan S, Sulsena, Tsinovit, Kelyual DS, Friederm Zinc, Danex, etc.
These funds help:
- reduce the number of fungi on the surface of the scalp and hair,
- reduce the amount of sebum produced,
- remove formed scales,
- inhibit cell division and the formation of scales.
All of the above properties of good shampoos for seborrhea are guaranteed by the presence in their composition of active ingredients that have antifungal, cytostatic, moisturizing and anti-inflammatory properties.
The main active ingredients of anti-seboric shampoos:
- Ketoconazole 1-2% - has antifungal effect, is used 2 times a week, is contraindicated until the age of 12,
- Ciclopirox 1-1.5% - has antifungal effect, it is used 1-2 times a week,
- selenium sulfide - acts destructively on the fungus,
- zinc pyrithione - eliminates inflammation, affects the fungus,
- medical tar - inhibits the growth of fungi and the formation of scales, eliminates inflammation and peeling of the scalp.
As a rule, medical shampoos are prescribed for 2-4 weeks. The frequency of their use may vary depending on the severity of symptoms. In some cases, it is recommended to use two medical shampoos (for example, one - containing antifungal drug, and the other with zinc).
In the composition of anti-seborrheic shampoos should not be present substances that contribute to the irritation of the skin. These include: parabens, aromatic fragrances, aggressive surfactants (SLESS, SLS), etc.
Dermatitis treatment
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis of the skin of the face is also very complex. In addition to eliminating the cause of dermatitis, the treatment of this disease includes a number of general recommendations for the normalization of nutrition and changes in the skin care regimen.
Features of skin care:
- Do not use aggressive skins and soap for washing.
- To cleanse the skin, use special gels or milk, which contain components that have antiseptic, antifungal and anti-inflammatory properties (for example, ketoconazole, tea tree oil, salicylic acid, zinc, selenium, lithium salts, hamamelis extract, quassia bitter, etc.) .
- Do not use alcohol-based lotions and tonics.
- The use of ointments and creams containing hormonal components is possible only under medical supervision.
Medical cosmetics
 Medical cosmetics for seborrheic dermatitis should be selected individually and used by courses that can be prescribed for the treatment of the disease, and for its prevention.
Medical cosmetics for seborrheic dermatitis should be selected individually and used by courses that can be prescribed for the treatment of the disease, and for its prevention.The most effective remedies for medical cosmetics are: Quasix gels and creams, Sesderma Sebovalis line, Uriage DS Gel Nettoyant cleansing gel, Bioderma, Sensibio product line, Tsindol and Zinocap.
Drug therapy
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis can be carried out according to various schemes, using various pharmacological preparations.
Tablets:
- antibacterial drugs (doxycycline, etc.),
- antihistamines (Citrine, Loratadine, Telfast, etc.),
- multivitamin and mineral complexes (Alphabet, Multitabs, Perfectil, Merz pills, vitamin A, B2 and C, nicotinic acid).
Medicinal ointments and creams:
- antifungal ointments (Nizoral, Mikospor, Bifam, Ketodin, Lamisil, etc.),
- hormonal ointments (Elokom and others),
- immunostimulants (Tacolimus, Elidel, Protopic, Pimecrolimus).
The doctor may also prescribe drugs for the normalization of the digestive system and the treatment of other associated diseases. With the defeat of seborrheic dermatitis of the eyelids and the development of blepharitis or conjunctivitis, eyelids and eyes are washed with antiseptic solutions, and the use of antibacterial eye ointments and drops.
Physiotherapy Physiotherapy treatments are also included in the complex therapy of seborrheic dermatitis. To do this, patients are assigned the following procedures:
Physiotherapy treatments are also included in the complex therapy of seborrheic dermatitis. To do this, patients are assigned the following procedures:
- darsonval,
- UV irradiation
- laser therapy
- cryotherapy.
Seborrheic dermatitis in children
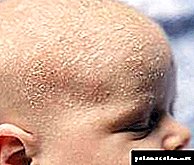
Seborrheic dermatitis in infants
Dermatologists differ in three degrees of the disease:
- I (mild form) - rash and gneiss (crusts) are located on the scalp, sometimes behind the auricles, on the forehead and cheeks, but the general condition of the child is not disturbed.
- II (moderate) - rash and gneiss spread to the body and limbs, the child becomes easily excitable, it can be observed diarrhea and frequent regurgitation.
- III (heavy) - 2/3 of the skin surface is covered with hyperemic, edematous areas of rash and gneiss. There is a secondary infection that causes weeping and suppuration, the child is lethargic or restless, eats poorly and does not gain weight, diarrhea is observed.
Seborrheic dermatitis in infants begins to manifest itself at 2 or 3 weeks of life. The child has elements of a rash on the skin of the scalp and, in rare cases, on the forehead, in the folds behind the auricles and on the cheeks. After a short period of time, gneiss appears on the rash sites, which is formed due to the accelerated shedding of epithelium cells and their impregnation with sebum.
Such areas of rash and gneiss can be localized in natural skin folds on the surface of the body. They are rarely accompanied by itching and are maculopapular rash, which is covered with fatty scales. As a rule, areas of seborrheic dermatitis in infants do not get wet.
When the treatment is not started on time, these areas of gneiss can grow and spread to any part of the body, but most often they are located on the scalp or in the perineum of the infant. When joining a secondary infection may develop pyoderma, accompanied by the release of exudate and painful sensations, provoking the restless behavior of the child.
With nutritional correction and timely treatment, the disease responds well to treatment, and its symptoms disappear either at 6-8 weeks of life, or at 7-8 months of age (sometimes by 1 year).
Seborrheic dermatitis in children older than one year
Seborrheic dermatitis in older children has symptoms similar to the manifestations of this disease in adults.
On areas of skin with a large number of sebaceous glands (the skin of the scalp, nose and nasolabial folds, forehead, cheeks, back and chest) a rash of a papular-squamous nature appears. After a short period of time, the rash is covered with scales stuck together with fat. When the upper layer is removed, areas of inflammation and redness are found on the skin. Foci of dermatitis may be subject to secondary infection with the subsequent development of pyoderma, otitis, blepharitis and other infectious complications.
Like seborrhea in adults, this disease in older children can pierce in liquid and thick form (i.e., there is a distinction between dry and oily seborrheic dermatitis in children). A characteristic feature of this disease in children is its chronic course with periods of exacerbation, which can be triggered by various predisposing factors (stress, exacerbations of chronic infections, immunodeficiency states, malnutrition, etc.).
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis in children under one year Seborrheic dermatitis in children under one year is well treatable and, in some cases, can disappear on its own by the 6-8 week of a child's life. For its treatment, it is recommended to strictly observe the rules of hygiene and apply means that contribute to the destruction of fungi and serve as prevention of the accession of a secondary infection.
Seborrheic dermatitis in children under one year is well treatable and, in some cases, can disappear on its own by the 6-8 week of a child's life. For its treatment, it is recommended to strictly observe the rules of hygiene and apply means that contribute to the destruction of fungi and serve as prevention of the accession of a secondary infection.
The doctor may recommend correction of the mother's diet if the baby is breastfed or in the baby.
In the absence of an allergic reaction to medicinal herbs, daily baths and headwashing using decoctions of chamomile, sage and calendula are recommended. After that, mineral or olive oil is applied to the lesions of seborrheic dermatitis, which promotes the gentle removal of crusts and has a beneficial effect on the baby’s skin.
After hygienic procedures, it is also recommended to apply Bioderma Sensibio D.S. on areas of the skin of the face, trunk and extremities affected by seborrheic dermatitis.
In the case of a secondary infection, the doctor may prescribe the use of antibacterial solutions for the hygiene of the affected areas and the application of antimicrobial ointments and creams.
In severe cases of seborrheic dermatitis in children under one year old children can be prescribed: vitamin therapy, immunostimulants, antifungal and hormonal ointments, antibacterial drugs, physiotherapeutic procedures.
Treatment of seborrheic dermatitis in children older than one year
Depending on the age of the child and the severity of symptoms can be applied:
- medicated shampoos with antifungal effect (Nizoral, Dermazole, Nizorex, Mycozoral, Sebasol, Ketoconazole, etc.),
- antifungal ointments and creams (Nizoral, Mikospor, Bifisam, Ketodin, Lamisil, etc.),
- hormonal ointments (Elokom),
- immunostimulants (Tacolimus, Elidel, Protopic, Pimecrolimus),
- antibiotics (doxycycline and others),
- vitamin therapy and taking mineral complexes (multivitamins, vitamins A, C, PP, zinc preparations),
- antihistamines (Diazolin, Loratadine, Citrine, Telfast, etc.),
- phytotherapy (use of decoctions and infusions of medicinal plants: nettle, calendula, birch buds, dandelion, burdock, etc.),
- dietary correction,
- physiotherapy (darsonval, UV, laser therapy, cryotherapy).
If necessary, consultations of narrow specialists (gastroenterologist, endocrinologist, gynecologist, etc.) can be prescribed. The duration of treatment and the dosage of drugs are prescribed individually by the doctor.
Diet for seborrheic dermatitis
 Successful treatment of seborrheic dermatitis in any form of this disease depends largely on the patient's proper diet. This is explained by the fact that the use of certain foods contributes to the growth of fungal flora and changes the chemical composition of sweat and sebum.
Successful treatment of seborrheic dermatitis in any form of this disease depends largely on the patient's proper diet. This is explained by the fact that the use of certain foods contributes to the growth of fungal flora and changes the chemical composition of sweat and sebum.
That is why from the diet should be excluded Some products and dishes:
- alcoholic beverages
- spicy, smoked, spiced and pickled dishes,
- fast food,
- products containing quickly digestible carbohydrates (flour and confectionery, sugary drinks, jam, rice, semolina, pasta),
- fatty and fried dishes,
- allergenic products (honey, nuts, citrus fruits, eggs, strawberries, etc.).
The use of other foods helps to normalize digestion, metabolic processes and speeds recovery from seborrheic dermatitis.
Wholesome products that must be included in the diet with seborrheic dermatitis:
- lean meats (veal, pork, white chicken meat, turkey, rabbit, lean fish),
- dairy products (natural fermented milk products, cottage cheese, low-fat cheeses, with good tolerance you can drink whole milk),
- baked and boiled vegetables (pumpkin, zucchini, cabbage, asparagus and broccoli are especially useful),
- berries (gooseberries, cranberries, white cherries, red and black currants, watermelon, etc.),
- vegetable oils (sunflower and olive).
Seborrheic dermatitis patients should pay close attention to adequate drinking water intake.
In some cases, the doctor may recommend a food diary, in which the patient will record their diet and reflect the severity of symptoms. The analysis of such a diary allows you to eliminate from the diet those foods that have contributed to the exacerbation of symptoms, and to achieve a more rapid recovery.
The manifestation of dermatitis in the scalp
Initially, when dermatitis occurs, the scalp is covered with dandruff. Without carrying out medical procedures, the disease progresses, passing to the next stage, which is characterized by redness, discomfort and sverbezh on the head sites. Combed wounds bleed and fester. The coat is quickly polluted, especially the root. Shampooing occurs much more frequently. After some time, the skin becomes covered with plaques, which are glued together between the sebum. Scraping scales, red, inflamed areas of the dermis open.
A long course of the disease provokes the progression of dermatitis. There is a loss of hair, baldness appears.
Dermatitis of the head is of two types: fat and dry. In the first case, the hair is in the stage of high fat. They quickly become soiled, washing is carried out daily. In the second case, a decrease in sebum, fragility, dryness and thinness of the hair bulb are observed. Dandruff is at the root of the hair.

Untreated dermatitis leads to baldness
Factors affecting the development of dermatitis
Human skin is a kind of barrier that blocks the path of pathogenic bacteria and fungi to the dermis layers. Sometimes this protective function can falter, weaken. As a result, yeast-like fungi start active reproduction. Dermatitis on the head may develop due to:
- Decreased functioning of the hormonal system. With an increase in the level of androgens in the blood vessels, the production of subcutaneous fat increases. Then there are inflammation of the dermis.
- Inherited factor. Very often, scalp dermatitis is a family disease. Weakened sebaceous gland activity is transmitted at the genetic level.
- Weakened immune system.Due to malnutrition and frequent colds, the protective mechanisms of the skin are reduced.
- Dysbacteriosis, chronic colitis, gastritis and other diseases of the digestive tract.
- Pathologies of the endocrine system.
- Chronic infectious foci developing in the body.
- Sharp change of climatic zones. As well as non-compliance with the rules of personal hygiene of the scalp.
- The use of shampoos, balms and gels that have an aggressive effect on the epidermis.
- Wearing hats made of synthetics.
- Neurological and Mental Illness. As well as sunburn and radiation damage.
Dermatitis on the scalp can affect the neck, eyebrows and eyelashes.

Synthetic headgear can cause dermatitis
Drug therapy
Treatment of dermatitis on the head is carried out by an experienced dermatologist. The specialist will determine the cause of the disease and select the appropriate drugs. If hormonal disorders are observed, the patient is examined by a neuropathologist and a gastroenterologist. To cure skin inflammatory processes by doctors apply:
- lotions, cream and balsam compounds with antifungal properties,
- hormonal medications,
- medical shampoos for hair, which include selenium, salicylic acid, tar and zinc,
- vitamin, tableted complex,
- antihistamines.
In addition, patients are assigned darsonvalization or cryomassage of the head. Procedures accelerate the process of separation of dead plaques, stabilize the level of adrenaline in blood vessels, improve the micro-circulation of the skin, reduce itching and burning.
Dermatitis treatment with ointments and creams
The treatment of dermatitis of the scalp should be approached comprehensively. This is due to the fact that specific drugs against the disease today do not exist. Only after determining the cause of the disease and its symptomatic manifestations, a course of treatment is prescribed. Inflammatory processes that are localized on the scalp are initially treated with antifungal shampoos Ketoconazole or Cyclopirox, as well as ointment or cream formulations. Consider the most effective drugs:
- Ointment "Hydrocortisone" is used for extensive lesions of the scalp. Properties of the drug can reduce the multiplication of the fungus, thereby accelerating recovery. Apply the drug no more than twice a day. Prolonged use of "Hydrocortisone" is not recommended, due to the high content of hormones.
- Ointment "Lamisil". Antifungal medication reduces the functioning of conditionally pathogenic microorganisms, relieves inflammation, has a peeling effect. Apply to the head covering in the morning and evening.
- Skin-Scap cream is used in the early stages of the disease. It contains the active substance zinc pyrithione, which helps eliminate dermal irritants.
Very often, immunomodulators are prescribed for the treatment of head dermatitis. Presented drugs are available in the form of creams. They prevent the proliferation of bacteria, reduce inflammation.
This group of drugs include cream compositions "Elidel", "Protopic". Dosage, duration of use prescribed by the doctor. Independent use of immunomodulators is not allowed.

Ointment "Hydrocortisone" stops the reproduction of the fungus
Tablets
In addition to external medications, oral medication may be included in the treatment regimen for dermatitis of the scalp. They are prescribed for a severe form of the disease in order to alleviate painful symptoms, eliminate extensive lesions of the dermis, and prevent secondary infection.
Today, the most effective drugs are:
The strongest corticosteroids are Prednisolone, Flumethasone, Dexamethasone. The presented remedies have antifungal effect, they actively fight against the main symptomatic manifestations of the disease. Acceptable use of short courses.
With advanced stages of dermatitis on the head, treatment is carried out with the help of immunosuppressants. The drugs inhibit the immune system, thereby lowering the severe skin reaction. The most effective medicines include "Cyclophosphamide" and "Chlorbutin". This type of medication is used at the very least when other medicines are powerless.
In addition to these drugs, a dermatologist may prescribe a vitamin complex. They will contribute to the rapid cleansing of the body from harmful toxins and slags, provide a quick recovery.

"Prednisolone" - a strong corticosteroid
Treatment of dermatitis in children
Before you begin treating dermatitis on the head of a baby, you should make sure that medical measures are necessary. With special care, inspect the skin, it is better to do it in the hour of bathing or combing. On the head should be only scales. If there are injuries, spots, acne, or wet secretions, then the child needs to be examined by a pediatrician.
The main treatment for dermatitis is regular, thorough shampooing. Today, pharmaceutical companies offer a huge range of anti-allergic shampoos. After using them, remove the flakes with a soft brush. Carry out the procedure with great care, so as not to damage the delicate skin. Never scrape the plaque with a nail, otherwise there is a risk of infection. The way to remove scales from the head of the baby:
- wash the baby's head with a healing shampoo,
- lubricate the skin is not flavored with oil,
- put on a hat
- wait 10 minutes
- after soaking and softening the crust, proceed to combing the plaques,
- use a soft brush.
When observing a severe course of the disease and joining a bacterial infection, expert help will be required. After the examination, the doctor prescribes taking antibiotics, glucose injections (intramuscularly), vitamin complex, ascorbic acids. When an infectious course of dermatitis in the child is the drainage of the peel from the skin of the head.

Ascorbic acid helps to overcome dermatitis in a child
Proper nutrition with dermatitis on the head
For the treatment to take place quickly and efficiently, the patient must follow a proper diet. Most people do not even realize that some foods provoke the growth of fungus and alter the chemical composition of sebum. For lesions of the skin is not recommended to use:
- alcohol,
- bitter and pickled dishes,
- smoked meat
- cakes and pastries,
- sweet soda,
- citrus,
- homemade honey
- Walnut,
- fried and fatty foods.
Try to eat as much as possible:
- lean meat (veal, chicken),
- cheese with a low percentage of fat, ryazhenka, kefir,
- baked vegetables,
- berries,
- sunflower oil and olive.
Do not forget about water consumption. With this disease, a person should drink at least two liters of purified fluid per day.
Timely treatment and compliance with all recommendations of the doctor will allow in the shortest possible time to eliminate dermatitis on the skin of the head.
Treatment with ointment and cream
Treatment of dermatitis on the head should be carried out in the complex. Such measures are necessary for the reason that there is no single remedy that can cure and get rid of dermatitis of any complexity and variety.
For a start, it is worth switching to special hair and scalp care products. The following shampoos are considered to be the most effective: ketocotonazole, cycloperix. In addition, it is recommended to use such creams and ointments:
- Hydrocortisone ointment. It is often used for large lesions of the scalp. This drug is able to eliminate the reproduction of the fungus, accelerate recovery. Ointment can be used twice a day, but it is forbidden to use a long period. This is due to the presence of a large amount of hormones in the composition,
- Lamisil. An ointment that serves as an antifungal agent. With it, you can eliminate pathogens, reduce inflammation. Also, the ointment is used for the peeling effect. It is recommended to apply it in the morning and evening, gently smearing the damaged areas of the scalp,
- Skin skap. Cream-gel, which is able to eliminate the manifestation of dermatitis, is most often used in the early stages. It contains zinc, which can eliminate irritation and soothe the scalp.
Additionally, the doctor may recommend the use of immunomodulators, which are also available in the form of a cream and gel. Such agents can relieve inflammation and serve as an antibacterial agent. These tools are used depending on the development of dermatitis of the scalp.
Drug tablets
In addition to the use of creams and gels, in the treatment of dermatitis include the use of tableted drugs. They can be prescribed for a severe form of the disease, with the aim of eliminating pain. Tablets help to eliminate large lesions of the dermis, as well as prevent the recurrence of infection.
Effective drugs consider:
The strong drugs that can be prescribed by prescription include: Prednisone, Flumetazon, Dexamethasone. These tools are used to quickly and effectively eliminate the fungus, quickly eliminate the symptoms of head dermatitis. They are usually prescribed in short courses. Additionally, the doctor may prescribe drugs to improve the intestinal microflora.
All tablets can affect the deterioration of the immune system, so doctors recommend an additional course of vitamins and minerals.
If the medications do not help, the doctor may prescribe potent drugs: Cyclophosphamide, Chlorbutin. They may also be prescribed for exacerbation of dermatitis, when other agents no longer cope.
Treatment in children
Before you start treating dermatitis in a baby, you should examine the scalp in detail. This can be done while bathing or combing. There may be only small crusts and peeling of the skin on the baby’s head, but if you observe injuries, redness, specks or pimples, you should contact your pediatrician and conduct an examination.
For the child, the main tool in the fight against dermatitis is frequent shampooing. To do this, there are many medications, but rather anti-allergenic shampoos. After washing, the scales should be removed. This should be done carefully, using a soft baby brush. You can remove scales in this way:
- rinse the head thoroughly with a medicated shampoo,
- use a special oil that needs to be spread all over the head and put a hat on,
- after absorbing the oil, the scales are easily removed with a brush.
Thus, the removal of plaques is quick and painless.
If the disease has passed into a severe stage, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics and therapeutic ointments. Additionally prescribed course of vitamins.
Treatment of dermatitis on the child’s head depends largely on the age and degree of complexity of the disease.
Disease diet
Proper dieting and good nutrition can help to cope with dermatitis on the head more quickly. Some foods can seriously affect the condition of the skin and can affect the change in sebum. If you are faced with dermatitis on any part of the body, in particular, and the head, you should avoid such products:
- Alcoholic beverages,
- Marinated dishes,
- Smoked products,
- Sweet,
- Soda and sweet water
- Citrus,
- Honey and nuts
- Fried
In the diet should be necessarily lean chicken meat, veal, dairy products with low fat content, vegetables, baked or boiled, berries, greens in large quantities. Olive oil is best for cooking.
When dermatitis should be aware of the use of water. During treatment, a person should drink at least 2 liters of water per day.
If you have a suspicion of dermatitis, you should immediately contact a specialist. Timely diagnosis will determine the cause of the disease and quickly resolve it.
With head dermatitis, you should not visit a hairdresser and beauty salons, because cosmetics can be harmful. Only an experienced doctor can prescribe the treatment and use of drugs. To make the treatment as effective as possible, you should stick to a diet and use the traditional method for treatment.
Stages of development and form
There are three forms of dermatitis:
The acute form is characteristic of the pathology of an allergic type. The disease of this type appears almost immediately after contact with an irritant. The symptoms of dermatitis disappear when the allergen is removed. Subacute form is characterized by the appearance on the body of papules and vesicles, which eventually become covered with crusts or scales. In chronic disease, there is an alternation of periods of remission and relapse, when the intensity of the symptoms increases.
The process of developing dermatitis goes through three stages:
- Erythrematous. At this stage, red spots and swelling appear in the problem area.

- Vesicular (vesicular). Edemas are replaced by various forms of neoplasms with liquid contents, which self-extinguish over time. This stage is known as oozing dermatitis.

- Necrotic. The last stage is characterized by the death of the affected tissues. In the problem zone at this stage, the skin becomes coarse.

Important! Not all types of dermatitis go through three stages of development. In particular, the allergic form often causes only redness and swelling of the skin.
Dermatitis, depending on the causative factor, are classified into: allergic, atopic (diffuse neurodermatitis), contact, seborrheic, toxic-allergic (toxicoderma), urtricaria (urticaria), solar, purpurous, bullous, infectious (dermatophytosis) and other forms.
Clinical picture
The nature of the clinical picture depends on the type of disease. Allergic form is manifested in the form:
- strong redness of the skin
- swelling,
- intense itching
- vesicular neoplasms.
Atopic dermatitis (eczema, diathesis) has a chronic form of flow and develops on the background of hypersensitivity to the effects of certain stimuli. Exacerbation of pathology often occurs in the cold season. The atopic form during relapse is characterized by the following features:
- papules, skin vesicles,
- peeling skin
- intense itching
- irritation, cracking of the dermis.
 Contact dermatitis develops due to exposure to stimuli:
Contact dermatitis develops due to exposure to stimuli:
- chemical substances,
- sunlight,
- pathogens,
- plants and more.
The contact form of pathology proceeds according to the type of allergic dermatitis.
Seborrheic type of disease localized mainly on the scalp. Pathology arises due to infection of the tissues with fungal microflora (ringworm). The activity of the latter is suppressed by the immune system. But in the presence of favorable factors, the following clinical phenomena begin to disturb the patient:
- red plaques on the scalp with clear contours,
- erythema,
- soak
- fissures and serous crusts on the skin surface,
- intense itching
- dandruff, hair loss,
- other symptoms characteristic of other types of dermatitis (dry, aural, etc.).
Toxidermia develops due to the penetration of allergens into the body (drugs, chemicals, food, etc.) that cause an allergic reaction. With this form of pathology, the patient has the following clinical phenomena:
- fever symptoms
- intense itching
- swollen lymph nodes
- skin rashes of various shapes and sizes.
In the case of the accession of a secondary infection, the nature of the clinical picture changes. On problem areas, there is suppuration of the rash.
Important! Often the condition of the skin is restored after eliminating the cause of inflammation. However, it is recommended to undergo a specialized examination to identify the factor that provokes the appearance of dermatitis.
Diagnostics
 Diagnosis of dermatitis is based on the results of the following measures:
Diagnosis of dermatitis is based on the results of the following measures:
- collecting information about the nature of food and possible contact with allergens,
- blood test,
- immune status assessment,
- study of scraping from the problem area,
- allergy tests.
If the specified diagnostic procedures did not allow to identify the causative factor, the patient is sent for examination to a gastroenterologist, therapist, psychotherapist.
Treatment of dermatitis involves:
- elimination of the stimulus,
- symptomatic treatment
- power correction,
- use of local and systemic drugs.
Regardless of the type of disease, patients are prescribed antihistamine medications:
 At the initial stage of development of the inflammatory process in the skin It is recommended to treat problem areas of the skin with hormonal creams or ointments:
At the initial stage of development of the inflammatory process in the skin It is recommended to treat problem areas of the skin with hormonal creams or ointments:
- Clotrimazole,
- Clobetasol,
- Advantan,
- 1% hydrocortisone ointment,
- Flucinar,
- Nizoral,
- Lamisil.
It is also necessary to regularly apply antiseptic solutions like Chlorhexidine or Erythromycin to the damaged areas of the child’s or adult’s skin. In the event of occlusion, it is recommended to apply a tissue moistened with Burov’s liquid to the affected dermis.
In the case of the dry form of the pathology, when the skin peels off in the problem area, the treatment of the affected areas with 5% sulfur-alicylic ointment is indicated. In the absence of the effect of the action of hormonal drugs used 2-3% naphthalene or ichthyol ointment.
Attention! To restore the skin of the head, it is recommended to abandon traditional shampoos in favor of specialized personal care products that have antifungal effects: Keto Plus, Nizoral Shampoo, Friderm Tar, Mycozoral.
 In case of infection of the scalp, drugs that suppress the activity of pathogenic microflora are prescribed. Selection of drugs is carried out taking into account the strain of the virus or fungus.
In case of infection of the scalp, drugs that suppress the activity of pathogenic microflora are prescribed. Selection of drugs is carried out taking into account the strain of the virus or fungus.
When dermatitis should be excluded from the daily diet foods that cause allergic reactions. Instead, it is recommended to consume food that strengthens the immune system. The list of products you need to check with a dermatologist.
Treatment of skin diseases is always carried out taking into account the cause of the disease. Therefore, if necessary, in the composition of drug therapy include other drugs.
Useful videos
How to treat dermatitis.
Contact dermatitis - causes, symptoms and treatment methods.
Causes of seborrheic form
From the early childhood, yeast-like fungi Malasseziya furfur are present on the skin and mucous membrane of a person. If the body for some reason (stress, illness) is weakened, it creates conditions for the rapid reproduction of fungi. The body is no longer able to cope with pathogenic microflora. Fungi consume sebum, so its excessive production, coupled with a decrease in immunity, allow mycosis to develop and spread much more than usual. As a result of such processes affects the skin and sebaceous glands, which leads to seborrheic dermatitis. Genetics also affects development. 
Diagnostic measures
A dermatologist establishes a clinical picture by examining and interrogating a patient. Conducted a complete blood count and analysis of hormones. It turns out the state of immunity.
In case of allergic dermatitis, the treatment takes place under the supervision of an allergist. In such cases, samples are taken in order to determine which stimuli have caused atopic dermatitis.
A visit to a gastroenterologist, an endocrinologist and a neuropathologist is recommended, as the disease often arises due to the presence of abnormalities of the gastrointestinal tract, diseases of the nervous nature and hormonal problems.
To cure atopic dermatitis, you need to find out the source of the allergic reaction and limit its effect on the patient.. Symptoms of allergies are struggled as follows:
- The patient needs a diet. Excluded from the diet: sugar, confectionery and other sweets, fast food, products containing caffeine, citrus fruits and strawberries, mushrooms, fish caviar. Consumption of fatty foods is not recommended. From the diet of children need to remove cow's milk.
- Drink plenty of water.
- The doctor selects a vitamin complex.
- Receiving antiallergic drugs - Loratadin, Suprastin.
- Medications for sedation: Glycine, Neuromedin, Nootropil.
It is recommended to coordinate the choice of shampoo with a dermatologist.. Since the effectiveness of treatment largely depends on this remedy, it is better to choose pharmacy options. Water for washing the head, it is desirable to insist on healing herbs, for example, on chamomile. For patients with dermatitis help shampoos containing tar, zinc (effective in the treatment of dry seborrhea), ketoconazole, ciclopirox. Popular brands: Nizoral, Keto-plus, Sulsena, Friederm Zinc.
After the symptoms have subsided, you should wash your hair with a shampoo twice a week for prevention. It is desirable that the composition had a minimum amount of flavors, colors and preservatives.
For the treatment of dermatitis, doctors prescribe various healing ointments, depending on the form of the disease.
- The atopic form is treated with glucocorticosteroid-based ointments - Hydrocortisone, Beclomethasone.
- For the treatment of seborrhea applied tar, salicylic and ichthyol ointment.
- After the disease subsides, the skin is softened with hyaluronic acid ointments - Solcoseryl, Curiosin, Libriderm.
Alternative Medicine
Folk remedies will help to cope with a fungal infection and poor performance of the sebaceous glands:
- Herbal decoction. For the preparation you will need the Hypericum flowers, the root of the elecampane and burdock, taken in equal shares. Two tablespoons of herbal medicine pour 250 ml of water, then boil for 10-15 minutes. Then you need to drain the liquid and cool. Infusion process the scalp, after washing it with a therapeutic shampoo.
- To reduce the excessive secretion of sebum and get rid of the scales can be using tea tree oil. One of the effective remedies is a hair mask. Five drops of tea tree oil and two drops of rosemary, lavender and bergamot oil are added to the base of two spoons of olive oil. You need to mix the ingredients and let them brew for five minutes. This mixture should be applied to the skin, wait 30 minutes and wash your hair with shampoo. You can add a couple of drops of oil in shampoo for washing hair.

- A decoction of onion peels. You need to take one and a half tablespoon of husk and boil it in 250 ml of water for 10 minutes, insist for half an hour, then strain. Next, you need to wet the broth with a piece of bandage and rub the scalp.
Before using any pharmacy or folk remedies, you need to test for the absence of allergic reactions. A drop of the selected drug is applied to the fold of the arm, waiting 30-40 minutes. If there is redness, burning or itching, you need to choose another medicine.